FACE ID is not recognized after makeup? iPhone X: My face is not so superficial!
Needless to say, last week's iPhone X was a fire in every headline. The biggest two points of view, one is the full screen (you need to know these before talking about iPhone X "AMOLED full screen"); then it is to take the Touch ID that has not been proud of the phone for a few years, and replace it with It is a very high-adjusted Face ID (face recognition), and the rivers and lakes are commonly called "brushing face".
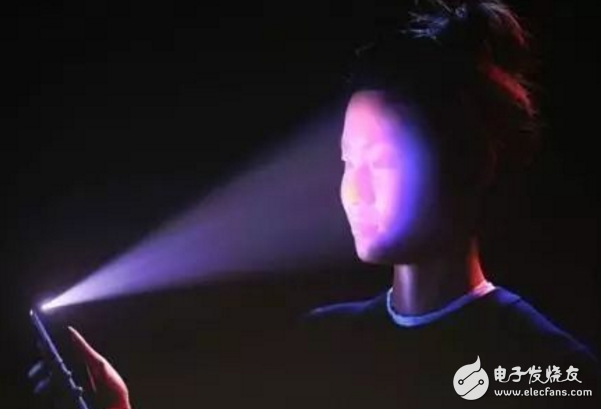

iPhone X's brush face function, ah no, it's Face ID
Although face recognition is not a new technology, it is arrogant and cool to implement on a mobile phone. However, once this feature was released, it was quickly questioned by a group of loved ones:
FACE ID is not recognized after makeup? iPhone X is haha, and said that the melons are still too young too simple, someTImes naïve!

The answer is of course no. Simply put, Face ID is based on 3D (deep) imaging technology, and does not look at the "skinny" "superficial", but by obtaining position information for 3D imaging. The basic component to implement this technology is the "depth camera" we will talk about next.
Depth camera: without me, 3D imaging can't be doneA depth camera is a special type of camera. Unlike a conventional camera, in addition to taking a flat image of an object, it can also measure the distance from the object to the camera position for 3D (depth) imaging.
There are three main principles: binocular imaging, structured light, and flight time.
Binocular imaging
The reason why our eyes can see stereoscopic images is because there are pupils in both eyes. When viewing objects at a certain distance, the two eyes will receive different visual images. The brain can subtly blend the two images with nuances through the movement and adjustment of the eyeball to perceive the physiological depth suggestion, resulting in a three-dimensional sense. This is the basic principle of binocular stereo vision.
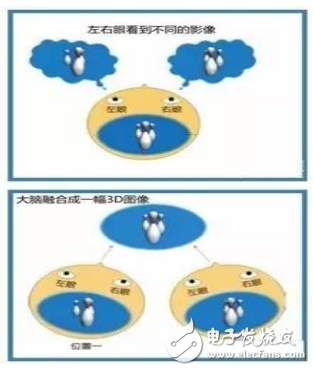
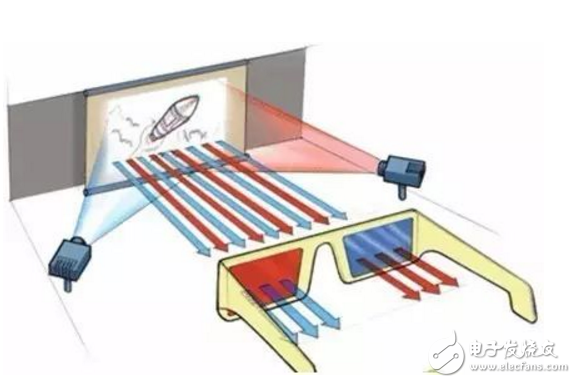
Familiar 3D movies are one of the applications of binocular stereo imaging principles
Binocular stereo imaging is based on this principle, acquiring, generating and transmitting a spatial scene and presenting the scene as a stereoscopic scene.
This is a more traditional technique that uses two visible light image sensors that can be achieved by binocular matching. Although this method has low cost and high image resolution, the algorithm is very complicated and is a passive measurement method. The target object needs to have good characteristic changes, otherwise it cannot be realized.
2. Structured light
The principle underlying the basic structured light scheme is the optical triangulation. The study found that when some special forms of light are cast onto objects with different depths, the texture of the light changes, and we can calculate the position and depth by collecting these texture changes, and then restore the entire three-dimensional space.

For example, when a light strip hits an object, the stripe of the protruding object will change its original state, or be broken, or bent, depending on the depth of each part of the object. Straight to the plane, the stripes do not change.
The structured light system is mainly composed of a light projection device (commonly known as near-infrared light), a camera, an image acquisition and processing system.
Among them, the camera uses an image sensor with a narrow-band filter and a lens to receive echo signals at different positions for imaging.
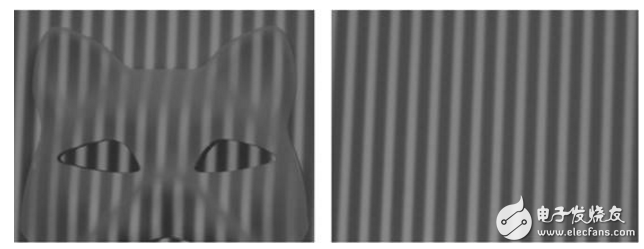
The picture on the right shows the modulated near-infrared streak light, and the picture on the left shows the grayscale image of the near-infrared CMOS image sensor.
The imaging quality of the first step directly affects the subsequent image processing, which requires the image sensor to have extremely high sensitivity in the near-infrared region, especially for some high-precision identification system applications.
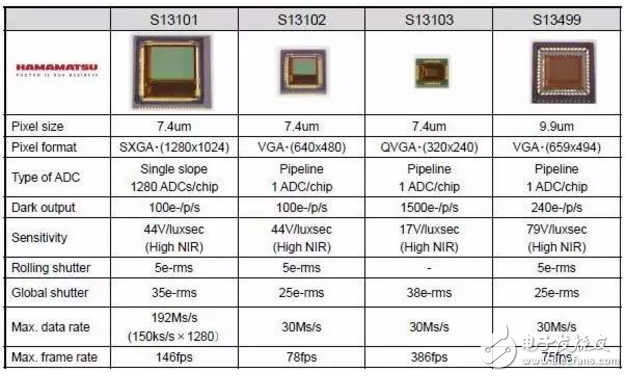
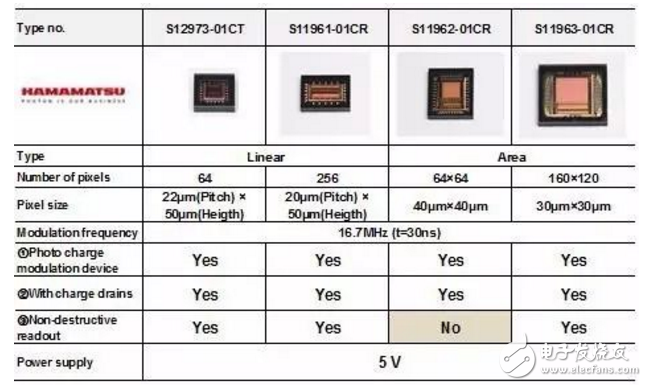
High sensitivity CMOS image sensor for Hamamatsu depth camera
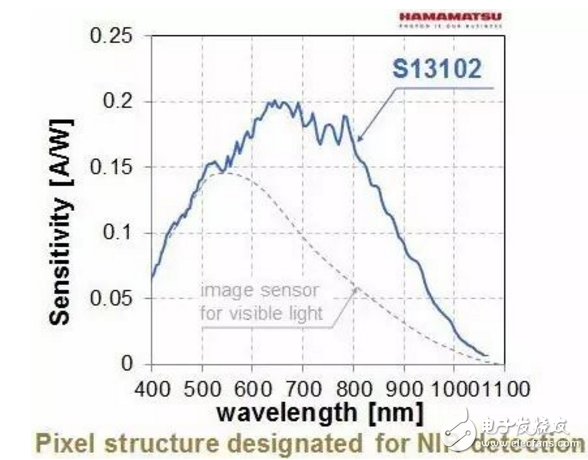

High sensitivity performance in the near infrared

High-speed capture capability
The next work after imaging is handed over to the image acquisition and processing system:
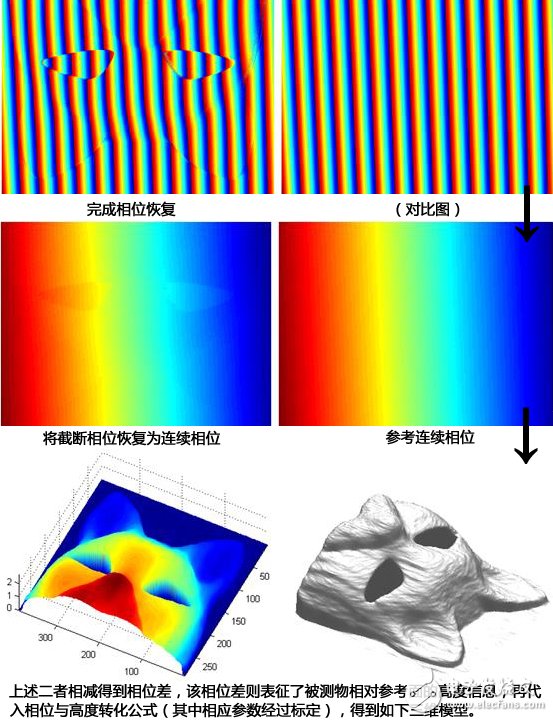
Source: The concept of structured light and what are the main principles for implementing 3D imaging? Lee Mr answers the content, knowing
The beam emitted by the laser passes through the optical system and is not only stripy, but also includes various speckle patterns including dots, single lines, single circles, concentric multi-circles, meshes, crosses, etc., and feature points are directly obtained by feature coding. As with ordinary stripe light, other feature patterns are also formed by forming a specific pattern on the scene, performing image processing after imaging, and then extracting pattern depth or distance information.
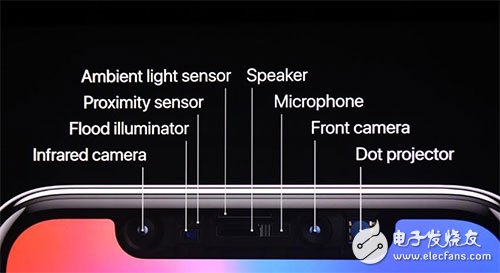
The iPhone X also uses the structured light to implement Face ID. Remember the "bangs" on the top of the screen? Placed in it is a system called "original deep-sensing camera". In addition to conventional devices, it also incorporates an infrared camera, a dot matrix projector, and a floodlight sensing element, which is the core component of Face ID. By projecting more than 30,000 optical information recognition points, the camera collects information and analyzes it by algorithm to realize its face recognition.
3. Flight time (TOF)
By capturing the time of flight from launch to reception, the object distance is determined. This is the common time-of-flight (TOF) method in ranging. In 3D imaging applications, the TOF method is implemented based on distance image sensors.
Each pixel of the image sensor chip records the phase between the incident light and the camera, and the sensor structure is similar to that of the ordinary image sensor, but includes two shutters for sampling the reflected light at different times, so the pixel size Larger than the average image sensor. In addition, the illumination unit and sensor require high speed signal control to achieve the desired accuracy.
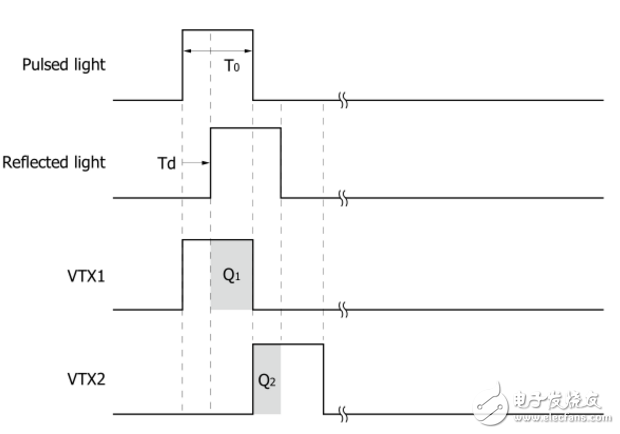
Hamamatsu TOF depth camera distance image sensor
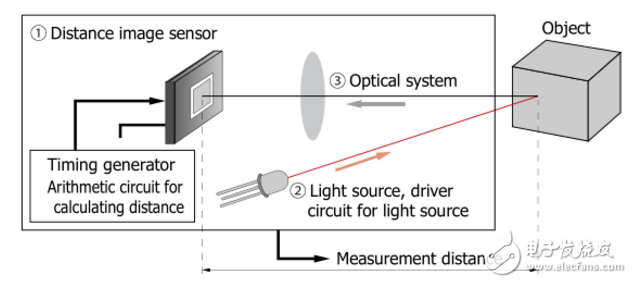
TOF's depth camera also consists of three parts, a high-speed light source (laser or LED), a distance image sensor that can test flight time, and a subsequent processing unit.
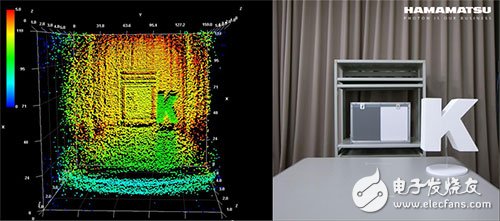
Left: Depth image (TOF method) / Right: Color image
Binoculars, structured light, and time of flight (TOF) are all common methods used in depth cameras, but they also have their own strengths:
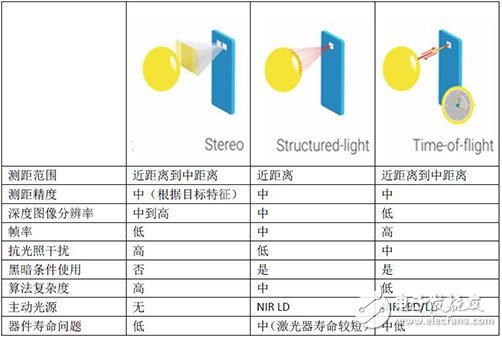
The difference in skill points also determines their respective areas of application. The binocular method has more restrictions on the external environment such as whether there is illumination or difference in the characteristics of the measured object, but it has a resolution advantage, and is more suitable for applications such as pipeline detection in which the environment is relatively simple; structured light can test relatively close distances, The requirements of the measured object are not high, and the depth resolution is taken into account, making it suitable for face recognition and somatosensory interaction in desktop devices or handheld devices. Although TOF is excellent in other aspects, it has depth image resolution. The low rate makes it more suitable for applications such as dynamic capture and robotic obstacle avoidance.
The emergence of the iPhone X Face ID has once again shaken the heat of 3D imaging, but it is only a representative of the torrent. In the future, 3D imaging is bound to become more popular, from consumer use to research, military, medical and other aspects, to change our lives.
SWITCH SOCKET
Guangdong Shunde Langzhi Trading CO., Ltd , https://www.langzhielectrical.com