Explain the basic concepts, fault handling, relay protection and integrated automation of En power system
1) Power system definition
A unified whole consisting of a generator in a power plant, a transformer and a transmission line in a power grid, and various electrical equipment of a user, connected according to a certain law, is called a power system.
2) The composition of the power system
The power system consists of a generator, a power grid, and a power user (powered equipment) in the power plant.
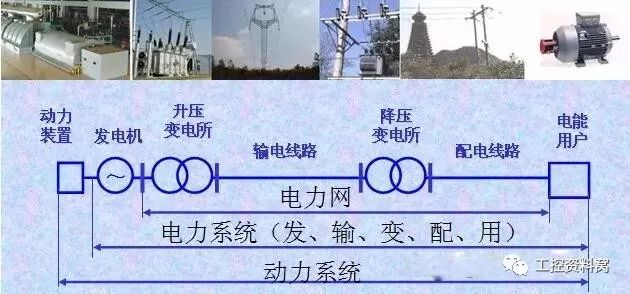
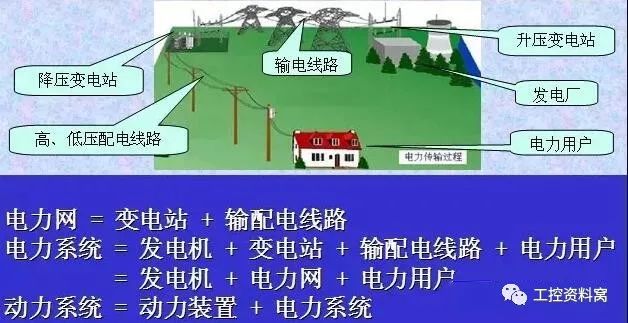
3) Power system voltage level
System Rated Voltage: The nominal voltage value of the voltage network at each level of the power system. The system rated voltage values ​​are: 220V, 380V, 3kV, 6kV, 10kV, 35kV, 63kV, 110kV, 220kV, 330kV, 500kV, 750kV.
4) Power equipment
The electrical equipment of the power system is divided into primary equipment and secondary equipment. The primary equipment (also called the primary equipment) is the main body of the power system. It is a device that directly produces, transports and distributes electrical energy, including generators, power transformers, and circuit breakers. , isolating switches, power bus, power cables and transmission lines. A secondary device is a device that controls, regulates, protects, and monitors a primary device, and includes a controller, a relay protection and an automatic device, a measuring instrument, a signal device, and the like. The secondary device obtains electrical contact with the primary device through the voltage transformer and the current transformer.
En power system failure and its harmAny connection or condition that causes the power system to malfunction is called a failure of the power system. There are many types of power system faults, such as short circuits, wire breaks, or combinations thereof. Short circuit is also called lateral fault, and disconnection is also called longitudinal fault. Short-circuit faults can be divided into three-phase short circuit, single-phase ground short circuit (referred to as single-phase short circuit) two-phase short circuit and two-phase ground short circuit. Note that two-phase short circuit and two-phase ground short circuit are two types of short-circuit faults of different natures. The short circuit current flows into the ground while the latter has. When the three-phase short circuit is still symmetrical, it is called symmetrical short circuit; other short circuits make the three-phase circuit asymmetrical, so it is called asymmetric short circuit. Broken wire faults can be divided into single-phase disconnection and two-phase disconnection. A broken line, also known as a non-full phase operation, is also an asymmetrical fault. In most cases, there is only one fault in the power system at a time, called a simple fault or a single fault, but sometimes there may be two or more faults occurring at the same time, called complex faults or multiple faults. Once a short-circuit fault occurs, it often has very serious consequences, mainly including: (1) The current increases sharply. The current during short circuit is much larger than the normal operating current, and can reach ten times the normal current in severe cases. The three-phase short-circuit current of the large-scale generator outlet can reach tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of amps. Such a large current will generate a huge impact force, which will deform or damage the electrical equipment, and at the same time, a large amount of heat will cause the equipment to overheat and be damaged. Sometimes an arc generated by a short circuit can directly burn the device. (2) The voltage drops significantly. When the three-phase is short-circuited, the voltage at the short-circuit point is zero, and the voltage near the short-circuit point also drops significantly, which will cause the power-consuming equipment to fail to work normally, such as the asynchronous motor speed drops or even stops. (3) The stability of the operation of the power system may be destroyed. After the short circuit of the power system, the electromagnetic power output by the generator is reduced, and the mechanical power input by the prime mover is not reduced correspondingly, so that unbalanced power occurs, which will cause the generator rotor to accelerate. Some generators accelerate faster, and some generators accelerate slowly, which makes the angle difference between generators larger and larger, which may cause the generators in parallel operation to lose synchronization, destroy the stability of the system, and cause power outages in large areas. . (4) Unbalanced current will flow in the system during asymmetric short circuit, which will induce high potential and large current in adjacent parallel communication lines, which may interfere with communication and may also cause danger to equipment and personnel. Among the above consequences, the most serious is the destruction of the parallel operation stability of the power system, which is referred to as the disaster of the national economy, followed by the sharp increase of current. In addition, some abnormal working conditions may occur in the power system. For example, if the electrical equipment exceeds the rated value (referred to as overload), it will also accelerate the aging of the electrical equipment insulation, causing hidden troubles and even developing into faults; The sudden load shedding of the generator, especially the hydro-generator, causes overvoltage of the stator winding, oscillation of the power system, failure of the cooling system of the power transformer and the generator, and frequency drop of the power system. Failures and abnormal operating conditions in the system may cause power system accidents, which may not only damage the normal operation of the system, but may even cause damage to electrical equipment and personal injury.
En power system relay protectionThere is a very close electrical or electromagnetic connection between the components in the power system. Once a component fails, electrical information will propagate around the system at approximately the speed of light. Such failures cannot be eliminated by manual manual methods and must be eliminated by means of high speed automation. This is the most effective way to ensure the safe operation of the power system. Power system relay protection is a technical discipline that studies such automatic devices that automatically identify faults and troubleshoot components. That is to say, the relay protection automatic device is an automatic device capable of reacting to an electrical component failure or abnormal operation state in the power system and acting on the circuit breaker to trip or issue an indication signal.
1) The role of relay protection
I. Automatically, quickly, and selectively remove the faulty component from the power system, so that the faulty component is protected from continued damage, and the fault-free part is quickly restored to normal operation. II. Respond to the abnormal operating state of the electrical components, and act to signal or trip according to the operation and maintenance conditions.
2) Relay protection device
When a power component (such as a generator, a line, etc.) in the power system or a power system itself fails to endanger the safe operation of the power system, a warning signal can be issued to the running duty person in time, or a trip command can be directly issued to the controlled circuit breaker. An automated measure and equipment to stop the development of these events. A complete set of equipment that implements such automated measures is generally referred to as a relay protection device.
3) Composition and working principle of relay protection device
The general relay protection device is composed of three parts: a measurement comparison component, a logic determination component, and an execution output component. I. Measuring comparison component: measuring the physical parameter passing through the protected power component and comparing it with a given value, giving a "yes", "not", "0" or "1" property according to the result of the comparison. A set of logic signals to determine if the protection device should be activated. II. Logic judgment component: According to the nature, sequence, duration, etc. of the logic signal outputted by the comparison component, the protection device determines the type and range of the fault according to a certain logical relationship, and finally determines whether the circuit breaker should be tripped and signaled. Or no action, and pass the corresponding instruction to the execution output part. III. Execution of the output component: according to the instruction sent from the logic judgment part, the trip pulse of the circuit breaker and the corresponding action information, the alarm or the non-action are issued.
4) Classification of relay protection
I. Classification by protected objects: transmission line protection, generator protection, transformer protection, busbar protection, motor protection, etc. II. Classification according to protection principle: current protection, voltage protection, distance protection, differential protection, direction protection, zero sequence protection, etc. III. Classification according to the types of faults reflected by the protection: phase-to-phase short circuit protection, ground short circuit protection, turn-to-turn short circuit protection, wire break protection, out-of-step protection, loss of field protection and over-excitation protection. IV. According to the implementation technology of relay protection devices: electromechanical protection, rectification protection, transistor protection, integrated circuit protection, and microcomputer protection. V. Relationship between measured value of relay protection and setting value: Excessive protection (measured value> setting value), under-protection (measured value <setting value) VI, classification by protection: main protection, backup protection, Auxiliary protection, etc. Main protection refers to the protection of system protection and equipment safety, and can selectively remove the protected equipment and line faults at the fastest speed. Backup protection refers to the protection used to remove faults when the main protection or circuit breaker is rejected. It is divided into near backup protection and far backup protection. Near backup protection: Two sets of protection are installed at the component. When the main protection is rejected, the other protection of the component is protected. Remote backup protection: When the main protection is refused, the backup protection is realized by another protection of the power equipment or the line; when the circuit breaker is rejected, the backup protection is realized by the breaker failure protection.
5) Basic requirements for relay protection
Selectivity, quickness, sensitivity, reliability; reliability means that the action should be taken when the action is protected, and not when it is not. Selective means that the fault is first removed by the protection of the faulty device or the line itself. When the faulty device or the protection of the line itself or the circuit breaker is rejected, the fault is allowed to be removed by the protection of the adjacent equipment, the line or the breaker failure protection. Sensitivity refers to the margin of correct operation capability of the protection device when a fault occurs within the protected range of the device or line, and is generally described by a sensitivity coefficient. Quick action means that the protection device should be able to cut off the short-circuit fault as soon as possible. The purpose is to improve the stability of the system, reduce the damage of the faulty equipment and the line, reduce the scope of the fault, and improve the automatic reclosing and standby power or standby equipment. Effect, etc.
En Substation Integrated Automation SystemUtilize advanced computer technology, modern electronic technology, communication technology and information processing technology to realize the functions of substation secondary equipment (including relay protection, control, measurement, signal, fault recording, automatic device and remote device) A comprehensive automation system that re-combines, optimizes, and monitors, measures, controls, and coordinates the operation of all equipment in a substation. Through the substation integrated automation system, the equipment exchanges information and data, and the substation operation monitoring and control tasks are completed.
Ground Screw For Other Buildings
High Dip Galvanized Ground Screw Pile made of carbon steel :Q235 ,according to standard ;DIN EN ISO1461-1999 ,not only used on the Solar Mounting projects,but also can be use for many other fields ,such as some temporary building,for timber,flage and banner,traffice sign ,for fencing construction ,for container house,for vineyard fencing ,for bridge & . it is easy to install ,no need digging ,no-concrete ,save time and cost .no harm to environment .
Due to their design and ease to installation,they are most commonly used wheneversoil conditons preventstandard foundation solutions,instead of requiring large excavationwork,they thread into the ground.
Construction Ground Screw,Hdg Ground Screw,Screw Anchor,Helical Pier,Ground Screw Anchor
BAODING JIMAOTONG IMPORT AND EXPORT CO., LTD , https://www.chinagroundscrew.com