Encoding, classification and application of the encoder
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts a signal (such as a bit stream) or data into a form that can be used for communication, transmission, and storage. The encoder converts an angular displacement or a linear displacement into an electrical signal, the former being called a code wheel and the latter being called a code ruler. According to the readout mode, the encoder can be divided into contact type and non-contact type; according to the working principle, the encoder can be divided into two types: incremental type and absolute type. The incremental encoder converts the displacement into a periodic electrical signal, which is then converted into a counting pulse, and the number of pulses is used to represent the magnitude of the displacement. Each position of the absolute encoder corresponds to a certain digital code, so its indication is only related to the start and end positions of the measurement, regardless of the intermediate process of the measurement.

According to the detection principle, the encoder can be divided into optical, magnetic, inductive and capacitive. According to its calibration method and signal output form, it can be divided into three types: incremental, absolute and hybrid.
1.1 Incremental encoder The incremental encoder directly outputs three sets of square wave pulse A, B and Z phases by photoelectric conversion principle; the phase difference between A and B pulses is 90 degrees, so that the rotation direction can be easily determined. The Z phase is one pulse per revolution and is used for reference point positioning. Its advantage is that the principle structure is simple, the average mechanical life can be more than tens of thousands of hours, the anti-interference ability is strong, the reliability is high, and it is suitable for long-distance transmission. The disadvantage is that the absolute position information of the shaft rotation cannot be output.
1.2 Absolute encoder Absolute encoder is a direct output digital sensor. There are several concentric discs in the radial direction on its circular disc. Each lane has a transparent and opaque sector. The sector tree of the adjacent code channel is doubled. The number of code channels on the code wheel is the number of bits of its binary digit. On one side of the disk is the light source, and on the other side, there is a photosensitive element corresponding to each code channel. When the disk is in different positions, each photosensitive element converts a corresponding level signal according to whether it is illuminated or not, and forms a binary number. The feature of this type of encoder is that it does not require a counter, and a fixed digital code corresponding to the position can be read at any position of the rotary shaft. Obviously, do you have to say N? At present, there are 16 absolute encoder products in China.
1.3 Hybrid absolute encoder hybrid absolute encoder, which outputs two sets of information, one set of information is used to detect the magnetic pole position, with absolute information function; the other set is completely the same as the output information of the incremental encoder.
Second, the application of photoelectric encoderThe difference between incremental encoder and absolute encoder
1, angle measurement
The car driving simulator uses a photoelectric encoder as a sensor for measuring the steering angle of the steering wheel. The gravity measuring instrument adopts a photoelectric encoder, and connects his rotating shaft with the compensation knob shaft of the gravity measuring instrument. The torsion angle meter uses the encoder to measure the change of the torsion angle, such as the torsion test machine and the fishing rod torsion fishing test. The pendulum impact test machine uses the encoder to calculate the impact as a change in the swing angle.
2, length measurement
The meter uses the circumference of the roller to measure the length and distance of the object.
The wire displacement sensor measures the length distance of the object by using the circumference of the winding wheel.
The coupling direct measurement is combined with the spindle of the power unit that drives the linear displacement, and is measured by the number of output pulses.
Media detection, in the straight rack, the chain sprocket of the rotating chain, the timing pulley, etc. to transmit linear displacement information.
3, speed measurement
Line speed, measuring the line speed of the production line by connecting to the meter
Angular velocity, measuring the speed of a motor, shaft, etc. by an encoder
4, position measurement
On the machine side, the coordinate position of each coordinate point of the machine tool, such as a drill press, etc.
In terms of automation control, the control performs the specified action at the pastoral position. Such as elevators, hoists, etc.
5, synchronous control
Through the angular velocity or linear velocity, the transmission link is synchronously controlled to achieve tension control.
Third, incremental encoder (rotary type)
1, working principle:
An optical code disc with a shaft at the center, with an annular pass and a dark engraved line, read by a photoelectric transmitting and receiving device, and four sets of sine wave signals are combined into A, B, C, D, each sine wave A phase difference of 90 degrees (360 degrees relative to a cycle), reverse the C and D signals, superimposed on the A and B phases to enhance the stable signal; and output a Z-phase pulse per revolution to represent the zero reference Bit.
Since the two phases A and B are 90 degrees out of phase, the encoder can be obtained by comparing the A phase before or the B phase to determine the forward and reverse rotation of the encoder, and the zero reference pulse can be used to obtain the zero reference position of the encoder.
The material of the encoder code disc is glass, metal and plastic. The glass code disc is deposited on the glass with a very thin engraved line. The thermal stability is good and the precision is high. The metal code disc is directly passed through and the line is not broken. However, due to the certain thickness of the metal, the precision is limited, and its thermal stability is one order of magnitude worse than that of the glass. The plastic code disk is economical, and its cost is low, but the accuracy, thermal stability and life are both poor. .
Resolution—The number of passes or dark lines that the encoder provides at 360 degrees per revolution is called resolution, also known as resolution indexing, or directly numbered lines, typically 5 to 10000 lines per revolution.
2, signal output:
The signal output has sine wave (current or voltage), square wave (TTL, HTL), open collector (PNP, NPN), push-pull type, TTL is long-line differential drive (symmetric A, A-; B, B -; Z, Z-), HTL is also called push-pull, push-pull output, the signal receiving device interface of the encoder should correspond to the encoder.
Signal connection—The pulse signal of the encoder is generally connected to the counter, PLC, computer. The modules connected to the PLC and the computer are divided into low-speed modules and high-speed modules. The switching frequency is low and high.
Such as single-phase connection, for single direction counting, single direction speed measurement.
AB two-phase connection, used for forward and reverse counting, judging forward and reverse and speed measurement.
A, B, Z three-phase connection for position measurement with reference position correction.
A, A-, B, B-, Z, Z-connection, due to the connection with a symmetrical negative signal, the current contributes to the electromagnetic field of the cable is 0, the attenuation is minimal, the anti-interference is optimal, and the long distance can be transmitted.
For TTL encoders with a symmetrical negative signal output, the signal can travel up to 150 meters.
For HTL encoders with a symmetrical negative signal output, the signal transmission distance is up to 300 meters.
3, the problem of incremental encoder:
Incremental encoders have zero point cumulative error, anti-interference is poor, the receiving equipment needs to be powered off, and the power should be changed to zero or reference position. These problems can be solved by using absolute encoder.
General application of incremental encoders:
Speed ​​measurement, measuring the direction of rotation, measuring the angle of movement, distance (relative).
Four, absolute encoder (rotary type)There are many optical channel engraving lines on the absolute encoder optical disc. Each line is arranged in 2 lines, 4 lines, 8 lines, 16 lines... so that each position of the encoder is read by each line. The pass and dark of the reticle, obtain a unique binary code (Gray code) from the zeroth power of 2 to the n-1 power of 2, which is called an n-bit absolute encoder. Such an encoder is determined by the mechanical position of the optical code disc, and it is not affected by power outages and interference.
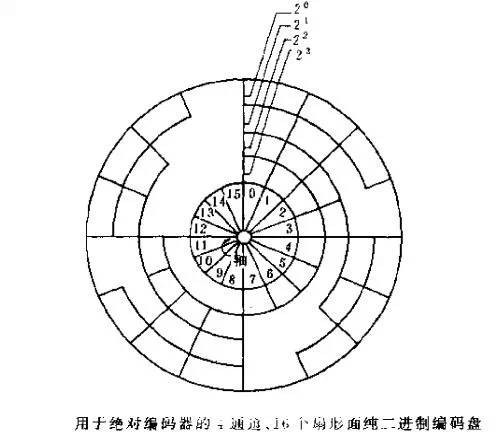
Absolute encoders are unique in each position determined by the mechanical position. They do not need to be remembered, do not need to find a reference point, and do not have to count all the time, when to know the position, and when to read its position. In this way, the anti-jamming characteristics of the encoder and the reliability of the data are greatly improved.
From single-turn absolute encoders to multi-turn absolute encoders
Rotate the single-turn absolute encoder to measure the scribe lines of the photoelectric encoder in rotation to obtain the unique code. When the rotation exceeds 360 degrees, the code returns to the origin, which does not conform to the principle of absolute coding. The code can only be used for measurements within a range of 360 degrees of rotation, called a single-turn absolute encoder.
If you want to measure the range of rotation over 360 degrees, you need to use a multi-turn absolute encoder.
The encoder manufacturer uses the principle of the watch gear mechanism. When the center code wheel rotates, another set of code wheels (or sets of gears, multiple sets of code disks) is driven by the gear, and the number of turns is increased on the basis of the single-turn coding. Encoding to expand the measuring range of the encoder, such an absolute encoder is called a multi-turn absolute encoder, which is also determined by mechanical position determination, and each position code is unique and does not need to be memorized.
Another advantage of the multi-turn encoder is that due to the large measurement range, the actual use is often richer, so that it is not necessary to find a zero point during installation, and an intermediate position is used as a starting point, which greatly simplifies the difficulty of installation and debugging.
The problem
Throughput is an important indicator of Ethernet testing. Many engineers believe that the Ethernet switching throughput should be its line rate, that is, no packet loss can occur at 100% traffic, and that it is illegal for the Ethernet frame interval IFG to be less than 96 bits. However, in the Ethernet switching throughput and packet loss rate test, a small amount of packet loss occurs in the long-term error test under the line speed condition. The reason is the cross-clock domain architecture of the Ethernet.
With the rapid development and application of industrial Ethernet technology, a large number of network problems have appeared along with it. According to statistics provided by Siemens, the network communication failure rate accounts for more than 70%, and the network equipment failure rate is less than 30%. After a network failure causes the system to shut down, the time required for fault diagnosis and location accounts for more than 80% of the total system downtime, while maintenance measures take up less than 20%. Therefore, real-time monitoring and analysis of network traffic is a major problem in the development and application of industrial Ethernet. Real-time monitoring and analysis of industrial Ethernet network traffic and timely detection and location of network problems play a vital role in improving the stable operation of the entire system. .
100M Switch,Fast Ethernet Switch,Fe Port,100M Ethernet Switch
Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com