WISP microchip with accelerometer and temperature sensor
Researchers at the University of Washington Sensing Laboratory have created a wireless identification and sensing platform, WISP. It is reported that WISP combines a sensor and a computing chip, which allows it to operate without a battery or a link power cord. It mainly absorbs the radio waves emitted by an RFID reader, which is a common anti-theft technology in retail stores, and converts radio waves into electric current.
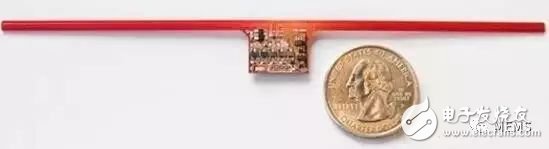
The coin-sized WISP wireless identification and sensing platform is known to have similar clock speeds and functions in WISP and Fitbit processors, including embedded accelerometers and temperature sensors. Aaron Parks, a researcher at the University of Washington's Sensing Laboratory, said that WISP can track sensory data and communicate with the outside world to do some basic information processing. It does this through backscattering wireless signals, Parks said, which is equivalent to using Morse code to communicate with lights. Surprisingly, according to Parks, the technology is quite fast. Its bandwidth is similar to Bluetooth low energy mode, a wireless charging technology that supports most Bluetooth speakers and wireless headphones. This gives WISP this new feature thanks to a team at Delft University: it can now rewrite code wirelessly. So, for example, a fitness tracker using WISP, now you don't need to connect it to any device, you can download new tracking features, or fix it to fix errors. This is amazing, no one has ever done it.
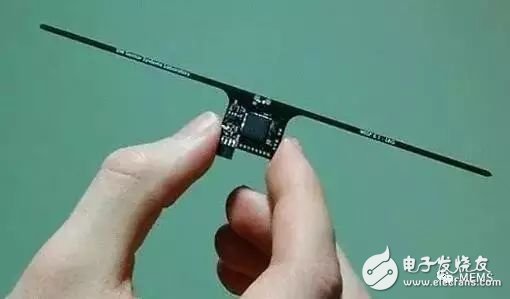
The batteryless computer chip WISPWISP is not the only batteryless computer chip. Parks said there are other sensors that don't require batteries, and they absorb any energy they can find, including passing TV waves, cell towers, and more. But now, these batteryless computers are very slow, and the distance can be programmed far away. By cooperating with WISP and RFID readers, Parks says they have been able to make 10x fast batteryless computers. What can these battery-free computers do? Parks says it’s still a long way to charge iPhones and laptops with radio waves. However, the area in which WISP can currently be used is architecture. By embedding these sensors in a reinforced concrete structure, the inspector can detect if the building has received damage during the earthquake. Parks also said that battery-free computers can also be used in implantable devices to monitor patient health. In addition, the agricultural sector is also interested in WISP computers, and its ability to simultaneously monitor thousands of plants can bring great value. There are also many consumer applications without battery computers, such as fitness bracelets. Parks said that you can even put a battery-free computer into your smartphone and send an emergency message when the device is out of power. However, the ultimate appeal of WISP and other battery-free computers is still in the Internet of Things, which can make devices smarter.
Aluminum Alloy LED lamps,Low Power LED lamps,LED line light
Kindwin Technology (H.K.) Limited , https://www.ktlleds.com